
In the world of web hosting, the choice of the operating system is a crucial decision. Linux, an open-source operating system, has become the backbone of many hosting solutions due to its exceptional stability, robust security, and unmatched flexibility. Whether you are setting up a simple personal blog, an e-commerce platform, or managing a complex corporate website, the Linux distribution you select plays a pivotal role in the overall success and efficiency of your hosting venture.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the best Linux systems for a wide spectrum of hosting applications, ranging from shared hosting to dedicated servers. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with the knowledge to make an informed decision about the Linux distribution that best suits your hosting needs.
Shared Hosting: Cost-Effective and User-Friendly
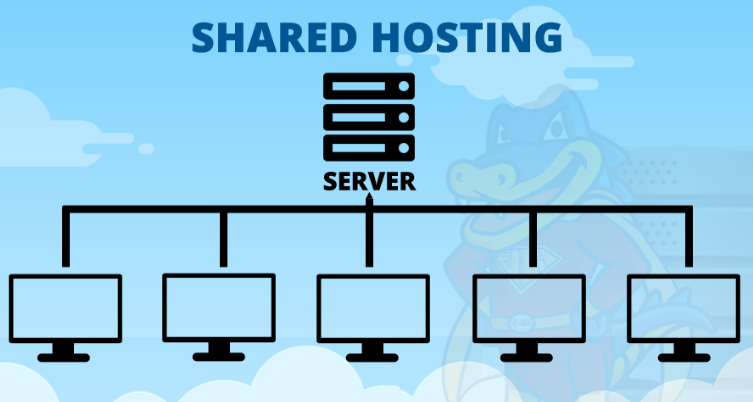
Shared hosting is an ideal starting point for individuals, small businesses, or those who need an affordable hosting solution. In this setup, multiple users share the resources of a single server, making it a budget-friendly choice. When selecting a Linux system for shared hosting, you should prioritize user-friendliness, security, and community support.
1. Ubuntu
Ubuntu, known for its user-friendliness and ease of use, is an excellent choice for shared hosting. It boasts a large and active community, ensuring you have access to help when needed. Frequent updates and security patches are other advantages, keeping your hosting environment secure and stable.
2. CentOS
CentOS is celebrated for its rock-solid stability and is derived from the open-source Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). It's a preferred choice for shared hosting, thanks to its robustness and long-term support.
Pros of Shared Hosting
- Cost-Effective: Shared hosting is one of the most affordable hosting options available. It is an excellent choice for individuals and small businesses with budget constraints.
- Ease of Use: Hosting providers typically manage server maintenance and technical tasks, making it user-friendly for those with little technical expertise. This includes tasks like server updates and security configurations.
- Low Maintenance: You don't need to worry about server management, as it's taken care of by the hosting provider. This allows you to focus on your website or application without the hassle of server administration.
- Technical Support: Shared hosting providers often offer customer support, so you can seek assistance with any hosting-related issues or questions.
- Scalability: Some shared hosting plans allow for easy upgrades as your website grows. You can start with a basic plan and scale up as your traffic and resource needs increase.
Cons of Shared Hosting
- Resource Limitations: Since resources are shared, the performance of your website can be affected by other websites on the same server. If one website experiences a sudden traffic spike, it could slow down your site.
- Limited Customization: Shared hosting environments are typically pre-configured, and customization options may be restricted. You may not have full control over server settings.
- Security Concerns: Sharing a server with other websites means that a security breach on one site could potentially affect others. While hosting providers implement security measures, there's always some level of risk.
- Limited Features: Shared hosting plans often come with limitations on features and the software you can use. This may not be suitable for websites with specialized needs.
- Performance Variability: The server's performance can vary, and during peak times, your website's performance may suffer. This can impact user experience and SEO rankings.
- Inadequate for High Traffic Sites: Shared hosting is generally not recommended for high-traffic websites or resource-intensive applications, as the shared resources may not suffice.
Virtual Private Servers (VPS): Enhanced Control and Resources
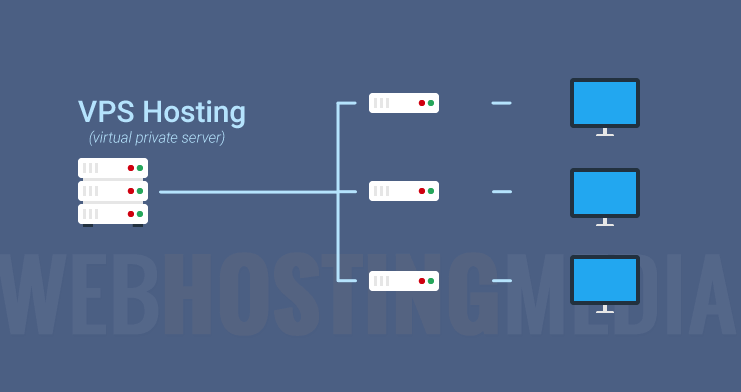
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a type of hosting that provides a middle-ground solution between shared hosting and dedicated hosting. It involves a physical server that is divided into multiple virtual servers using virtualization technology. Each VPS operates as an independent server with its own resources and operating system. VPS hosting offers more control, privacy, and flexibility compared to shared hosting, making it a popular choice for a wide range of users.
1. Debian
Debian is highly stable and provides a large repository of packages, making it a strong choice for VPS hosting. Its reputation for reliability and its active developer community contribute to its popularity.
2. Fedora
Fedora is renowned for offering the latest software packages and features, making it a great choice for advanced users who seek cutting-edge technology. If you want access to the latest tools and are comfortable managing your VPS, Fedora is worth considering.
Pros of Virtual Private Servers (VPS):
- Increased Control: VPS hosting provides users with more control over server settings and configurations. You can install and customize software, manage security settings, and make changes to suit your specific needs.
- Dedicated Resources: Unlike shared hosting, where resources are shared, a VPS guarantees dedicated resources like CPU, RAM, and storage. This ensures consistent performance and reduces the risk of performance bottlenecks caused by other users.
- Isolation and Security: Each VPS is isolated from others on the same physical server, enhancing security. A security breach on one VPS does not affect others. You can also implement your security measures.
- Scalability: VPS hosting is easily scalable. You can adjust resources as your website or application grows, allowing for increased flexibility and accommodating changes in traffic and usage.
- Customization: VPS hosting allows you to fully customize your server environment. You have control over the choice of the operating system, software, and configurations, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Affordability: While more expensive than shared hosting, VPS hosting is still cost-effective for small to medium-sized businesses and websites with moderate traffic. It offers a balance between performance and cost.
Cons of Virtual Private Servers (VPS)
- Technical Knowledge Required: Managing a VPS may require more technical expertise than shared hosting. You need to be comfortable with server administration and configuration.
- Resource Limitation: While VPS provides dedicated resources, there are still limits. High-traffic websites or resource-intensive applications may eventually outgrow the resources allocated to a VPS.
- Responsibility for Maintenance: You are responsible for server maintenance, including updates, security patches, and backups. This means investing time and effort in keeping the server running smoothly.
- Cost: VPS hosting is more expensive than shared hosting. While it provides more value and control, the cost can be a limiting factor for some users.
- Performance Variation: Although VPS hosting reduces performance issues caused by other users, the overall performance may still vary depending on the hosting provider, hardware, and the number of VPS instances on a physical server.
- Limited Control Compared to Dedicated Servers: While VPS hosting offers a higher level of control, it still falls short of the full control and resources available with a dedicated server.
Dedicated Servers: Unmatched Control and Resources

Dedicated servers are hosting solutions where an entire physical server is dedicated to a single user or organization. This means that all the server resources, including CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth, are exclusively available for the user's use. Dedicated servers offer the highest level of control, privacy, and performance, making them an excellent choice for resource-intensive applications and large websites.
1. CentOS
CentOS's robustness and predictability make it a top choice for dedicated servers. Its long-term support and stable release cycle are particularly valuable for server management.
2. Debian
Debian's reliability extends well into dedicated server environments, where security and dependability are paramount. Its flexibility and customizability appeal to those who want fine-grained control over their server.
Pros of Dedicated Servers
- Unmatched Performance: Dedicated servers provide the highest level of performance. With all server resources dedicated to a single user, your website or application can handle heavy traffic and resource-intensive tasks without performance bottlenecks.
- Complete Control: Users have full control over server settings, configurations, and software installations. This level of control is ideal for customizing the server to meet specific requirements.
- Security: Dedicated servers offer a high degree of security. Since no other users are sharing the server, the risk of security breaches due to neighboring websites is eliminated. You can implement your security measures and configurations.
- Customization: Dedicated servers allow complete customization. Users can choose their preferred operating system, software, and hardware, tailoring the server environment to their specific needs.
- Resource Scalability: Most hosting providers offer scalable dedicated server plans. Users can upgrade or downgrade server resources as needed, providing flexibility as their requirements change.
- Reliability: With dedicated resources, the server is more reliable, as there are no fluctuations in performance due to the actions of other users.
Cons of Dedicated Servers
- Cost: Dedicated servers are the most expensive hosting option due to the exclusive use of hardware resources. This can be a limiting factor for small businesses and individuals with limited budgets.
- Technical Expertise Required: Managing a dedicated server demands a high level of technical expertise. Users are responsible for server maintenance, including software updates, security patches, and troubleshooting.
- Time-Consuming: Server management can be time-consuming, and users need to invest time and effort in maintaining and optimizing the server. This can be a significant commitment.
- Complexity: The complexity of server management can be daunting for individuals or businesses without dedicated IT staff. Some users may need to hire professionals for server administration.
- Overkill for Small Websites: Dedicated servers are excessive for small websites or applications with low traffic. Paying for resources you don't fully utilize can be inefficient.
- Limited Scalability: While many hosting providers offer resource scaling, there are limits to how much a dedicated server can be upgraded. In cases of significant growth, you may need to consider more complex hosting solutions.
Cloud Hosting: Scalability and Resilience
Cloud hosting is a flexible and scalable hosting solution that leverages virtualized resources from a network of interconnected servers. Unlike traditional hosting, where websites and applications are hosted on a single physical server, cloud hosting distributes resources across multiple virtual servers, ensuring redundancy, scalability, and high availability. This hosting model has become increasingly popular due to its adaptability and reliability.
1. Amazon Linux
Amazon Linux is designed for use on Amazon Web Services (AWS) and is optimized for the cloud. It ensures top-notch performance and reliability, making it an ideal choice for cloud-based hosting.
2. OpenSUSE
OpenSUSE is known for its high configurability, making it well-suited for cloud deployments. Its adaptability and ability to meet the evolving needs of a dynamic cloud environment make it a valuable choice.
Pros of Cloud Hosting:
- Scalability: Cloud hosting offers unparalleled scalability. Users can easily adjust resources up or down based on their needs, accommodating traffic spikes or changes in usage without downtime.
- Reliability: Cloud hosting relies on a network of interconnected servers, ensuring high availability. If one server fails, another takes over, minimizing downtime and increasing reliability.
- Pay-as-You-Go: Many cloud hosting providers offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where users only pay for the resources they consume. This flexibility is cost-effective, especially for businesses with variable resource requirements.
- Performance: Cloud hosting services typically provide excellent performance with high-speed data centers and optimized configurations.
- Global Reach: Cloud providers often have data centers in multiple geographic locations, allowing users to host their websites and applications closer to their target audience, improving load times and user experience.
- Security: Cloud hosting providers invest heavily in security measures, including data encryption, firewalls, and regular security audits, making it a secure hosting option.
Cons of Cloud Hosting
- Cost Complexity: While pay-as-you-go pricing can be cost-effective, it can also be complex to manage. Users need to monitor their resource consumption to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Data Privacy: Cloud hosting involves storing data on servers owned by a third party, which can raise concerns about data privacy and control, especially for highly sensitive information.
- Technical Knowledge: Managing cloud hosting environments can be complex and may require a high level of technical expertise, particularly when optimizing resources and configuring servers.
- Latency: Although cloud hosting offers excellent global reach, some users may experience latency issues if their data is located far from their users. Choosing the right data center location is crucial.
- Limited Customization: Cloud hosting platforms may have limitations on customization compared to dedicated servers. Users may not have the same level of control over server settings.
- Resource Sharing: In multi-tenant cloud environments, there is some level of resource sharing, which can impact performance during high-demand periods. Premium cloud plans mitigate this, but it's still a consideration.
Conclusion
Choosing the best Linux system for your hosting needs involves a nuanced evaluation of various factors, including your technical expertise, the specific requirements of your website or application, and the hosting environment in which you operate. The Linux distributions discussed in this article cater to a wide range of hosting scenarios, from shared hosting ideal for beginners to dedicated servers suited for advanced users.
It's important to note that regardless of your choice, ongoing maintenance and updates are paramount to the security and performance of your hosting environment. As technology continues to evolve, so will the best Linux systems for hosting. Stay informed about the latest developments in the Linux ecosystem to ensure your hosting setup remains optimized and secure.
Your choice of a Linux system is pivotal to your hosting venture's success. With the insights provided in this guide, you are better equipped to make an informed decision, ensuring your hosting environment aligns seamlessly with your unique hosting goals. Remember, the right Linux distribution can make all the difference in your hosting experience.




Comments (0)
No comment