
Introduction
Digital data has become a big part of our lives for the last decade, and it shows no signs of stopping at any point in the future. Backing up your data is the process of copying your data and storing it in a safe place to be used in case the original version faces any problems. These issues can be ransomware attacks, accidental deletions, or hardware failures. If you encounter such a problem, you can restore your data using your backup. This makes backing up your data very important to ensure the smooth running of all operations.
Since data backup and recovery is a hot topic in the digital world due to World Backup Day, we’re bringing you a comprehensive guide on Data Backup and Recovery and why it is essential to back up your data. So without further ado, let’s dive in!
The Risks of Not Backing up Data
Not backing up your data can adversely affect you in many ways. Here are the most common risks associated with not backing up your data.
1. Data Loss

One of the most severe consequences of not backing up your data is the risk of permanently losing critical data. This loss can happen for various causes, such as hardware failure, inadvertent removal, or natural disasters. The loss of valuable data can have long-term, negative consequences for your company's operations and production.
2. Decreased Productivity

If you don’t back up your data regularly, it can lead to you losing your data at critical junctures. Recovering your data, especially if you don’t know what to do, can be time-consuming. This affects your productivity in many different ways.
3. Financial Loss

Not backing up your data can result in you facing heavy financial losses, both directly and indirectly. You can expect immediate economic consequences if you lose sensitive financial information, client information, trade secrets, etc.
Other than that, you can also face indirect financial consequences. These can be the time and money spent on data restoration attempts, reduced productivity, and lost business potential and prospects.
4. Legal Consequences

Depending on your business type, you can face legal consequences if you fail to back up your data adequately. For example, you might risk penalties and consequences if your business deals require you to adhere to stringent compliance standards. This is especially true for people working in sectors like banking, healthcare, education, etc., that deal with personally identifiable information of your customers.
Methods of Data Backup
Now that we’ve looked at the risks associated with not backing up your data, let’s move on to the options you have to back up your data. You can use many methods to back up your data and keep it secure.
1. Local Backup (External Disks)

If you want to back up your data for personal use, using external hard drives and storage devices can be a great way to back up and secure your data for easy access locally. This is true if you don’t want to risk uploading your data on a cloud forum. You can use hard drives, SSDs, flash drives, etc., for this data backup method.
Professionals like video editors, videographers, and YouTubers commonly use this method. That is because it lets you have all your data on hand if needed.
Here are some external hard drives and storage devices that we recommend if you’re going to use this method of data backup:
- WD Elements Desktop Hard Drive
- Seagate Backup Plus Ultra
- SanDisk Extreme Pro Portable SSD
Although local media can be backed up to an external disk using the default operating system, we recommend using a dedicated third-party software such as EaseUS Todo Backup to make the process seamless and quick.
2. Cloud-Based Backup Solutions

The first method we’ll discuss is Cloud backup, an online or remote backup. It’s a strategy for backing up your data by storing a copy of a physical or virtual file or database in a secondary, off-site location. This is done mainly via websites or SaaS tools, and this method can be beneficial if you suddenly face issues due to equipment failure, site disaster, or human error.
Most cloud backup providers charge a subscription fee for storage access (as well as add-ons in the form of managed backup and recovery services), with prices relevant to your storage volume and bandwidth consumption. Cloud-based backup has become the primary method for backing up critical data, especially for large companies, due to ease of use and rapid restoration times.
The most well-known cloud-based backup solutions are:
- iDrive
- Backblaze
- Acronis
3. Local Network Backups
Another method for backing up your data is using local network backups. If you don't want to back up your data to a cloud or an external drive, a regional network backup is your best bet–especially if you're using a local area network or NAS. You can either manually back up your data every time or set up an automated backup for your files or system.
We’d recommend you go with the latter option because an automated backup can free you from remembering to back up your data regularly. It also reduces the time your maintenance and backup tasks take in half.
Here are some of the best ways to back up your data on a local network:
- NAS Backup
- A computer on your LAN
4. Hybrid Backup Solutions
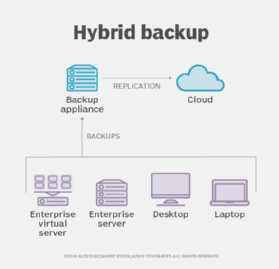
Another method of backing up your data is to use a hybrid backup solution. Hybrid backup solutions combine cloud and backup methods to provide a comprehensive backup facility. If you deal with a lot of sensitive data for your work or if your work is about databases, virtual machines, or SaaS applications, this method can be the best option. Using a hybrid backup allows you to have redundancies in your backups as well as a flexible option for restoring your data if you need to.
Many prominent hybrid backup solutions are on the market today, and you can use them quite easily to secure your data. Some of the hybrid backup solutions we recommend are:
- AWS Outposts
- Google Anthos
- Azure Stack
- VMware Cloud
Best Practices for Data Backup
Since we've discussed the risks associated with not backing up your data and methods of data backup in the previous sections, let’s look at the best practices for data backup that you should observe and follow. These practices can help you keep your data safely backed up and available for restoration. Here are some of these practices that we recommend you observe.
1. High Frequency of Backups
One of the main things you need to do to create backups for your essential data efficiently is to increase the frequency of your backups. Usually, people consider backing up their data weekly or monthly (mostly done overnight) to be enough of a redundancy. However, more is needed due to the continuously evolving cybersecurity challenges we face in the digital world today.
According to our trials and tests, you should try to back up multiple times daily. However, we also understand that only some deal with data significant enough to warrant such a high backup frequency and the facilities required to store such a vast amount of data. Therefore, we recommend you back up your data daily to limit any complications you could face due to data loss.
2. Use Backup Methods Tailored to Your Needs
You can use many methods to back up your data, as we have also discussed in the previous section. Depending on your requirements and the size and type of data you usually work with, you might need different types of backups. Therefore, you must use the data backup method that is the best for you and your work. For example, if you run a SaaS or database, using only a cloud-based backup instead of a hybrid backup can lead to you facing big problems, leading to monetary loss and hurting your business’ reputation.
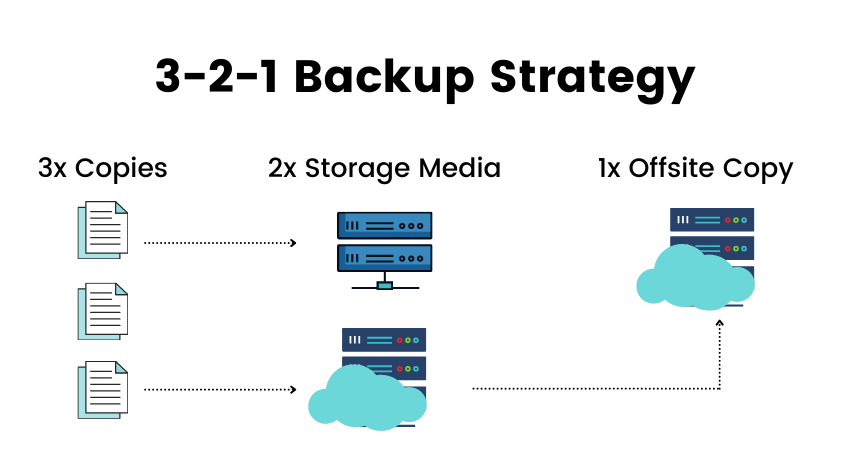
3. Follow the 3-2-1 Backup Rule

The most important practice for data backups is to follow the 3-2-1 backup rule, especially if you are backing up the data of a company or an organization. This rule states you should have at least three updated copies of your data for backups. Out of these three copies, you should store two on-site using different storage media (e.g., one copy on an external drive and one on a NAS or LAN).
Meanwhile, the 3rd copy should be kept outside the company’s premises. This can be done relatively quickly via cloud backup nowadays. Organizations dealing with sensitive data (governments and militaries, for example) usually manually store the 3rd copy off-site in a secure location instead of trusting it to a cloud-based service.
Conclusion
In this post, we have discussed data backup and recovery and why it is essential to back up your data. We have discussed the risks associated with not backing up your data, the best methods for data backup, and the best practices you should follow when backing up your data. After reading this article, we hope you have enough information about data backups to ensure that you choose the best backup method for yourself and prevent yourself from losing your important data due to any mishap.
Share this post
Leave a comment
All comments are moderated. Spammy and bot submitted comments are deleted. Please submit the comments that are helpful to others, and we'll approve your comments. A comment that includes outbound link will only be approved if the content is relevant to the topic, and has some value to our readers.

Comments (0)
No comment